刚进公司的时候,一直是使用nginx作为静态页面web服务器。其实nginx另一个更大作用是软负载均衡。 优点:
1、高吞吐,官方称单台nginx服务最大能支持100000并发连接,这是理论值实际可能达不到,看网上人家测试一般单台30000以上并发连接是没问题的。
2、廉价:和动辄10多万F5相比,nginx免费开源,对于几台机器的集群来讲性价比更高更合适。
3、低内存消耗:nginx处理请求是异步非阻塞的,在高并发下nginx 能保持低资源低消耗高性能。一般情况下,10 000个非活跃的HTTP Keep-Alive连接在Nginx中仅消耗2.5MB的内存,这是Nginx支持高并发连接的基础。
动手感受一把吧! 准备工作:三台centos虚拟机,两台用于部署tomcat,一台用于部署nginx。
一、部署两台tomcat
tomcat部署需要jdk环境,此处不再赘述jdk如何部署。 准备了192.168.127.10和192.168.127.11两台主机部署tomcat
1.下载tomcat
wget http://mirrors.hust.edu.cn/apache/tomcat/tomcat-8/v8.5.24/bin/apache-tomcat-8.5.24.tar.gz
2.解压、启动
解压后修改默认主页,方便识别
tar -zxvf apache-tomcat-8.5.24.tar.gz
cd apache-tomcat-8.5.24
./bin/start.sh
3.scp一份到另一台主机,启动
scp -r apache-tomcat-8.5.24 root@192.168.127.11:/usr/local/src/
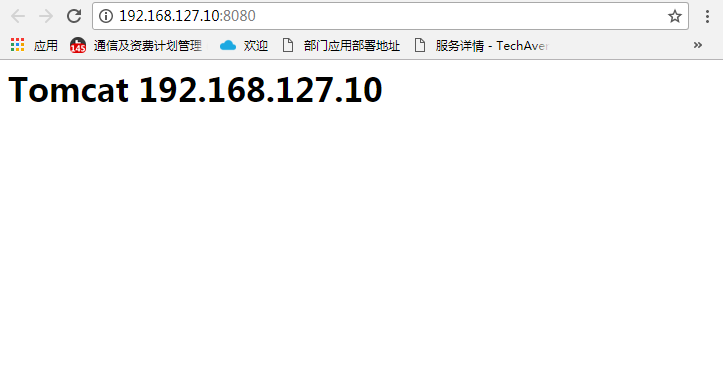
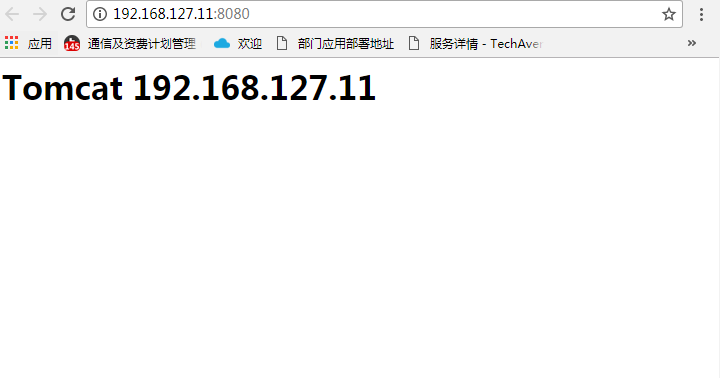
二、部署nginx
192.168.127.12用于部署nginx
1、gcc 安装 安装 nginx 需要先将官网下载的源码进行编译,编译依赖 gcc 环境,如果没有 gcc 环境,则需要安装:
yum install gcc-c++
2、PCRE pcre-devel 安装 PCRE(Perl Compatible Regular Expressions) 是一个Perl库,包括 perl 兼容的正则表达式库。nginx 的 http 模块使用 pcre 来解析正则表达式,所以需要在 linux 上安装 pcre 库,pcre-devel 是使用 pcre 开发的一个二次开发库。nginx也需要此库。命令:
yum install -y pcre pcre-devel
3、zlib 安装 zlib 库提供了很多种压缩和解压缩的方式, nginx 使用 zlib 对 http 包的内容进行 gzip ,所以需要在 Centos 上安装 zlib 库。
yum install -y zlib zlib-devel
4、OpenSSL 安装 OpenSSL 是一个强大的安全套接字层密码库,囊括主要的密码算法、常用的密钥和证书封装管理功能及 SSL 协议,并提供丰富的应用程序供测试或其它目的使用。 nginx 不仅支持 http 协议,还支持 https(即在ssl协议上传输http),所以需要在 Centos 安装 OpenSSL 库。
yum install -y openssl openssl-devel
5、下载nginx、解压
wget -c https://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.10.1.tar.gz
tar -zxvf nginx-1.10.1.tar.gz
cd nginx-1.10.1
6、配置 此处我们使用默认配置
./configure
7、编译安装
make
make install
至此,nginx已经安装完毕。
三、配置nginx
修改配置文件nginx.conf
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
upstream my_project_nginx{
# ip_hash;
server 192.168.127.10:8080 weight=1; #weight是权重的意思,权重越大分配概率越大。
server 192.168.127.11:8080 weight=1;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
proxy_set_header Host $host:80; #端口跟上面的一致
proxy_set_header REMOTE-HOST $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_pass http://my_project_nginx; #此处my_project_nginx和上面的upstream my_project_nginx对应
client_max_body_size 10m;
client_body_buffer_size 256k;
proxy_connect_timeout 600;
proxy_send_timeout 600;
proxy_read_timeout 600;
proxy_buffer_size 32k;
proxy_buffers 4 64k;
proxy_busy_buffers_size 128k;
proxy_temp_file_write_size 512k;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
}
启动
./sbin/nginx
四、运行集群效果
打开nginx服务地址http://192.168.127.12/,刷新页面发现没有任何变化,看了半天的配置文件没有发现问题,原来是浏览器缓存在作怪。Chrome调试模式下清除缓存重新加载出现预期效果,如下图:
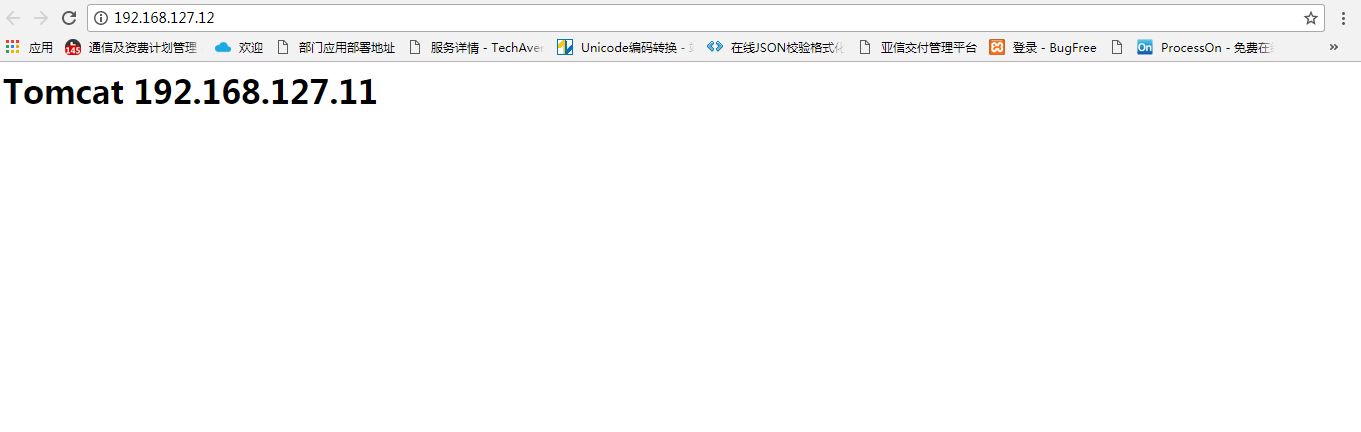
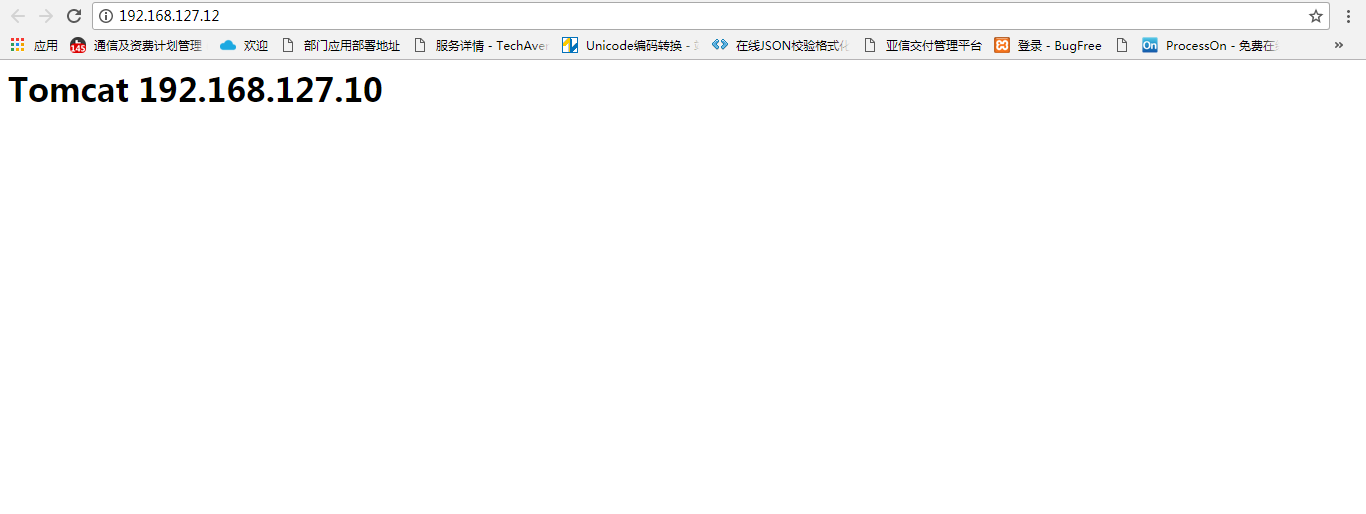
五、拓展 负载均衡规则
1、轮询(默认) 每个请求按时间顺序逐一分配到不同的后端服务器,如果后端服务器down掉,能自动剔除。
2、weight 指定轮询几率,weight和访问比率成正比,用于后端服务器性能不均的情况。 例如:
upstream bakend {
server 192.168.127.10 weight=1;
server 192.168.127.11 weight=1;
}
3、ip_hash 每个请求按访问ip的hash结果分配,这样每个访客固定访问一个后端服务器,可以解决session的问题。 例如:
upstream resinserver{
ip_hash;
server 192.168.127.10;
server 192.168.127.11;
}
4、fair(第三方) 按后端服务器的响应时间来分配请求,响应时间短的优先分配。
upstream resinserver{
server 192.168.127.10;
server 192.168.127.11;
fair;
}
5、url_hash(第三方)
按访问url的hash结果来分配请求,使每个url定向到同一个后端服务器,后端服务器为缓存时比较有效。 例:在upstream中加入hash语句,server语句中不能写入weight等其他的参数,hash_method是使用的hash算法
upstream resinserver{
server 192.168.127.10;
server 192.168.127.11;
hash $request_uri;
hash_method crc32;
}